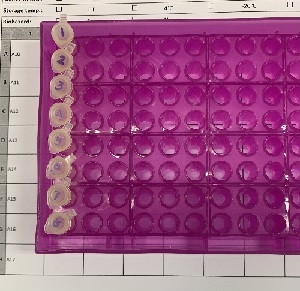
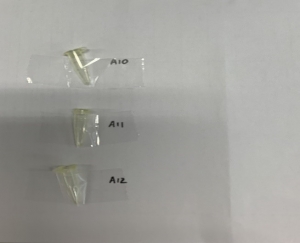
Use 200uL microtubes (sample less than 8) OR 8-well strip (sample less than 32)
Workflow
Sample Preparation
Good Sequencing Result Requires High Quality DNA
DNA Preparation
Plasmid DNA
Plasmid DNA should be free from genomic DNA, RNA and other impurities.
Various standard plasmid purification methods can be used.
Commercial plasmid purification kits (column-based) usually work well.
PCR product
PCR product must be pure and of one specific sequence in order to obtain unambiguous sequencing reads.
For best results, primers, primer-dimers and dNTPs should be removed before using the PCR products as template DNA for sequencing. Different methods can be used for such clean-up:
- Column purification*
- Agarose gel purification
- Enzymatic (e.g. Exo-SAP IT) purification
*Check cleanup size cut-off of column used.
Any COLOURED PCR pre-mix reagents are not recommended as the coloured dye might affect the sequencing results.
DNA QC
DNA quality and quantity can be checked by agarose gel electrophoresis with proper DNA mass ladder.
Plasmid DNA and purified PCR product concentration can be determined by UV spectrophotometer (e.g. Nanodrop) or fluorescence-based method (e.g. Picogreen or Qubit). A260/280 ratio >1.8~2 reflects pure DNA.
Primers, primer-dimers and dNTPs contribute to A260 reading, thus concentration of PCR product with such contaminants will be overestimated by UV spectrophotometer (e.g. Nanodrop) measurement.
DNA Template and Sequencing Primer Pre-mix Guidelines
DNA template and sequencing primer must be mixed (pre-mixed) before submitting for sequencing.
Prepare 15 µL of pre-mixed for submission with the following procedures:
- Aliquot appropriate amount of template DNA*.
- Add 1 µL of 5 µM sequencing primer..
- Top up to 15 µL with DNase-free water.
*The guideline shows the appropriate amount of template DNA:
| Sample Type | Total DNA amount in 15 µL sample (ng) | DNA concentration in 15 µL sample (ng/µL) | |
| PCR Product | 100 - 200bp | 1 - 3 | 0.07 – 0.20 |
| 200 - 500bp | 3 - 10 | 0.20 – 0.67 | |
| 500 - 1000bp | 5 - 20 | 0.33 – 1.33 | |
| 1000 - 2000bp | 10 - 40 | 0.67 – 2.67 | |
| > 2000bp | 20 - 50 | 1.33 – 3.33 | |
| ssDNA | 25 - 50 | 1.67 – 3.33 | |
| dsDNA, Plasmid | 150 - 300 | 10.00 – 20.00 | |
| Cosmid, BAC | 500 - 1000 | 33.33 – 66.67 | |
| Bacterial genomic DNA | 2000 - 3000 | 133.33 – 200.00 |
It is NOT recommended to use TE or other EDTA-containing buffer in the pre-mix, also AVOID adding any divalent cations, such as Mg2+, Ca2+, and Mn2+, etc.
*Users submitting template-primer pre-mix OR finished cycle sequencing product should optimize the template/primer ratio OR cycle sequencing reaction condition, which is specific to the template size/content and primer binding efficiency.
CPOS cannot be responsible for sequencing failure due to sub-optimal template/primer ratio OR cycle sequencing condition.
The following standard cycle sequencing programme will be applied.
| Temperature | Time | Cycle |
| 96ºC | 1 min | 1 |
| 96ºC | 10 sec | 25 |
| 50ºC | 5 sec | |
| 60ºC | 4 min | |
| 10ºC | Infinite | 1 |
Purification & Capillary Electrophoresis
Submit 20 µL of cycle sequencing reaction product. Volume can be made up with DNase-free water.
The final volume MUST BE 20 µL or samples will be rejected. Protect cycle sequencing product from light.
Sample Submission
Sample Submission Format
To ensure efficient processing of samples and speedy services, samples MUST be submitted in designated vessel types.
| Sample Quantity | Vessel Type | |
| 1 to 7 | 200 µL microtubes |  |
| 8 to 32 | 8-well strip with caps |  |
| 33 to 90 | 96-well plate* (arrange samples by column, i.e. fill down A1-H1 -> A2-H2 and so on) Leave 6 empty wells for in-house run controls (refer to Sanger Sample Submission Form) *If you are using courier delivery service (for local non-HKU academic users only), plate MUST be sealed by strip caps tightly. If submitting plate in person without flipping, good quality adhesive film is acceptable. |  |
Please adhere to the above format and label the tubes/strips/plates clearly.
Sample Submission Procedure
Please refer to the “How a user makes a service request (Sanger Sequencing)” section for further information.
- Prepare samples according to the vessel type as described above.
- Submit service request through iLab.
- Fill in Sanger Sample Submission Form.
- Use one form per plate
- Fill in ALL information clearly or job will be delayed
- Expected read length for each sample is required for data QC
- Submit Sanger Sample Submission Form as attachment through iLab.
- Submit samples to the core, with a hard copy of the completed Sanger Sample Submission Form stapled on the outside of the plastic bag.
DOs and DON’Ts for Sample Submission
Do NOT use 1.5mL microtubes
Label sample tubes with number correspond to sample name on the sample submission form.
Put samples into plastic bag.
Do NOT write the samples ID on paper and tape the samples to the paper.
Staple the sample submission form outside of the plastic bag.
Do NOT put the sample submission form inside plastic bag.
Sample Collection Boxes
There are three off-site DNA sequencing sample collection boxes installed for your convenience.
The CPOS offers daily sample pick-up service from the three sample collection boxes.
While CPOS will try to ensure sample security by providing boxes with locks, we shall not be responsible for any sample losses.
If your samples are precious, we recommend bringing them to our counter in person during office hours.
Do NOT drop off samples after pick-up time on Fridays, Saturdays and the day before holidays.
Sample Submission by Courier Delivery
Local non-HKU academic users should arrange courier delivery for sample submission by themselves. Please refer to below for details of the receiver’s information:
Receiver’s information:
- Contact Person: CPOS
- Contact number: 2831-5500
- Address: 6F, HKJCBIR, 5 Sassoon Road, Pokfulam, HK
- Company Name: Centre for PanorOmic Sciences (CPOS)
Payment Method: Sender Paid (寄付)
Seal the strip/plate with strip caps.
Pack the samples in a sealed envelope.
Note: CPOS should not be held liable for any loss or damage of sample during delivery.
Data Collection
DNA Sequencing results are delivered to users as zipped file through Online Data Delivery System (ODDS), notification will be sent to the email provided on the service request form upon data delivery.
Our current turn-around time is 1-3 working days after sample submission. However, the turn-around time could be longer at times due to unforeseeable circumstances and busy sequencing schedules.
We recommend Sequencing Analysis Software for viewing the electropherograms, and SeqScape Software to perform sequence comparisons on variant identification, SNP discovery, and SNP validation.
Both software are available on our user data analysis workstations (User PC#2) in Room 6-01 at the Centre for PanorOmic Sciences (CPOS).
Users may make advanced bookings for the workstations via our online resource booking system (ORBS) or at our reception counter (6-02).
Alternatively, Sequence Scanner Software can be freely downloaded from ABI website. It is also a great tool for reviewing sequencing data.
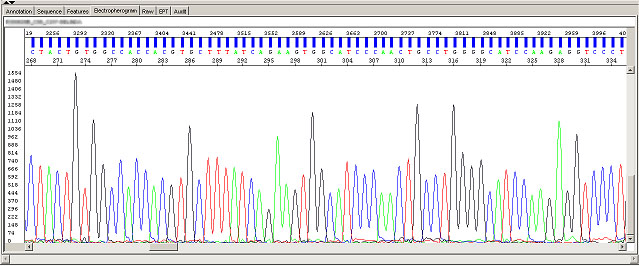
DNA Sequencing Analysis using the Sequencing Analysis Software from ABI
Terms of Service
At CPOS, positive and negative controls are included for every step in every run to monitor cycle sequencing, purification and electrophoresis quality.
Data from every run are reviewed and results will only be released to clients if all controls passed in-house QC.
Please refer to “Data QC” page for the rationale, charging scheme and details for rerun request.
The “Troubleshooting” page will help you evaluate the need for rerun.
CPOS can provide consultations including a suitable protocol that may improve sequencing results.
Our goal is to give you the highest quality of sequencing data possible.
Data QC
According to our sequencer manufacturer, there exists up to 10% sporadic instrument-associated failure due to:
- random bad/insufficient injection
- bubble in the capillary during polymer filling
- cross-capillary fluorescence due to the nature of capillary sequencing and the proximity of the capillaries to each other (~5um) in the detection cell of the 3730xl platform
CPOS offers complimentary default reruns for sequencing samples with sporadic instrument-associated failures or sub-optimal data.
Users could also request for rerun of the samples. However, for samples with strong intensity, the charging scheme is shown below:
| Rescued | NOT Rescued | |
| Original run | Normal charge | Normal charge |
| Rerun | HK$ 0 | HK$ 20 |
The rescue criteria are defined as:
- CRL improved by ≥ 30%, with an absolute increase of 50bp, OR
- Overall TS improved by at least 5, with a value at least 35
CRL: Contiguous Read Length is the longest uninterrupted stretch of bases with quality higher than 20.
In the evaluation of the quality of each base, not only the quality value of individual base is used, but also those of adjacent bases within a window size of 20.
TS: Trace Score is the average basecall quality value of bases in the post-trim sequence.
Users should review their own data and exercise discretion before requesting reruns.
The “Troubleshooting” guide will offer assistance in making an informed decision.
Users are also welcome to consult our platform specialists on difficult cases.
CPOS reserves the rights for final discretion over borderline cases.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting guide
Always check raw signals and sequence tracing when evaluating sequencing results.
The following images were generated by ABI Sequence Scanner, which is available for free download on ABI website.
Click here for software installation instructions and operations.
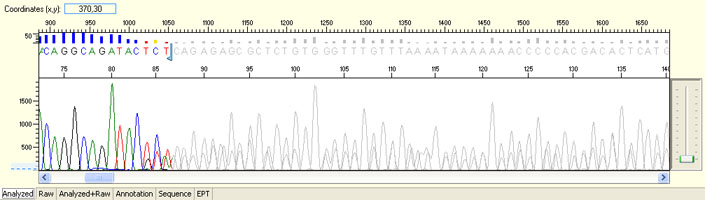
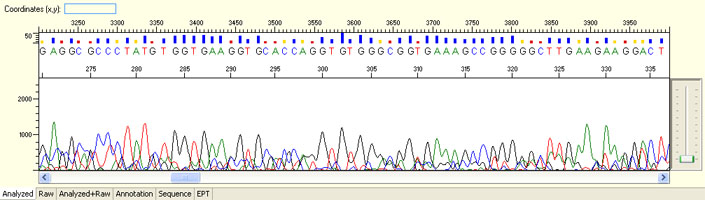
Result:
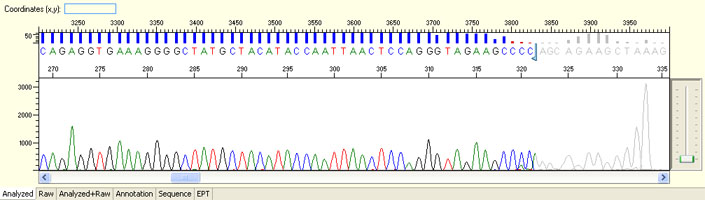
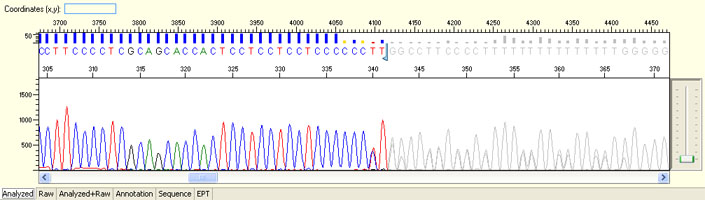
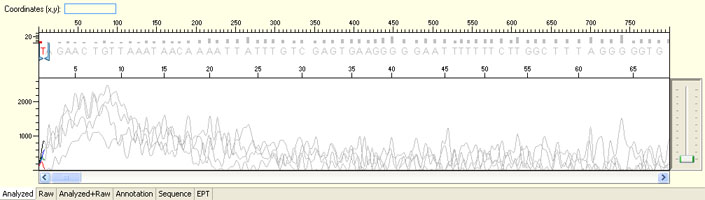
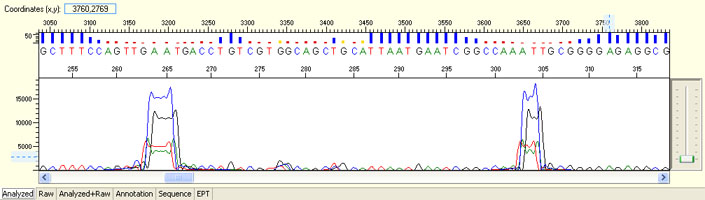
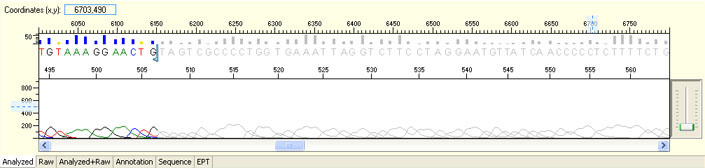
Long read for plasmid
- Good quality read till 800-1000 bases
- Clean/flat baseline
- Relatively even raw signal level across the whole read length, gradual drop is normal
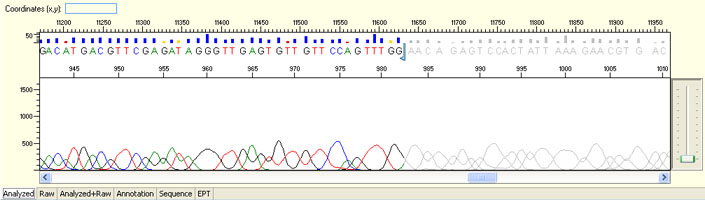
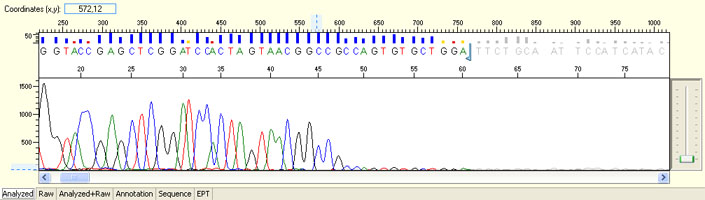
Short read for PCR product
- Good quality read along the length of the PCR product up to around 1000 bases
- Clean/flat baseline
- Relatively even raw signal level across the whole read length, gradual drop is normal
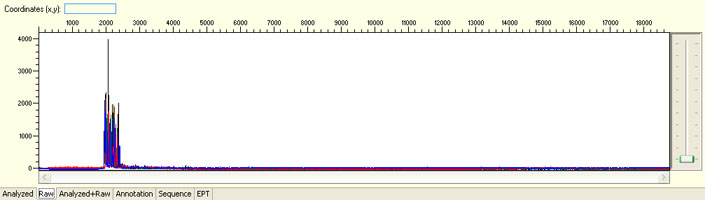
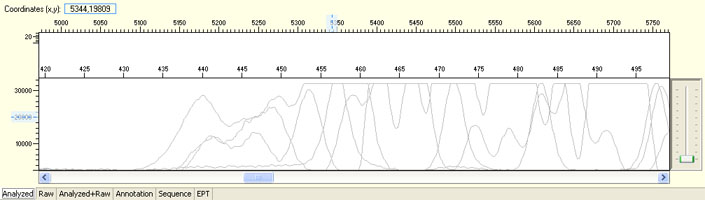
Signal dropped soon after read start
Possible Causes
- Primer-dimer formation
- Secondary structure
- High GC-content
- Inappropriate template/primer ratio
Possible Solutions
- Re-design sequencing primer to avoid primer-dimer formation
- Re-design sequencing primer to sequence the opposite strand
- Optimize cycle sequencing conditions and submit purification & run samples
- Optimize template/primer concentration
Signal dropped soon after read start
Poly C/T
Poly G/T
Possible Causes
- Replication slippage
Possible Solutions
- Optimize cycle sequencing conditions and submit purification & run samples
- Re-design sequencing primer to avoid homopolymer region
- Re-design sequencing primer to sequence the opposite strand
“Top heavy” Signal
Possible Causes
- Too much DNA template/Too much primer
- Salt or ethanol contamination
- High concentration of EB, EDTA
Possible Solutions
- Quantify DNA and follow our sample submission guidelines to prepare premixed samples
- Perform extra ethanol wash when purifying DNA
- Dry spin column/DNA pellet longer before eluting DNA
- Elute DNA in Elution buffer (10mM Tris-Cl, pH 8.5) or nuclease free H2O
Overlapping sequences after a short clean read
Possible Causes
- Non-homogeneous template, e.g. more than one plasmid
Possible Solutions
- Sub-clone again and ensure a single colony is picked
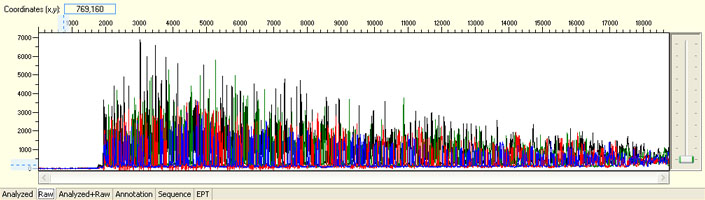
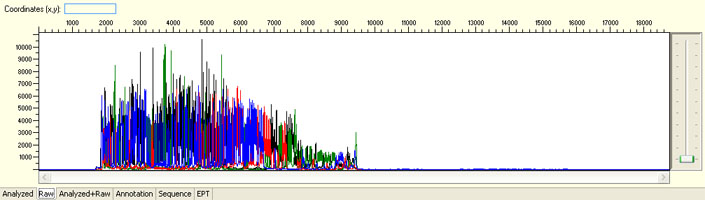
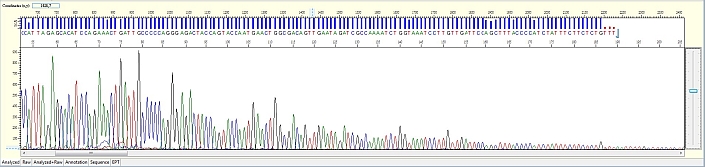
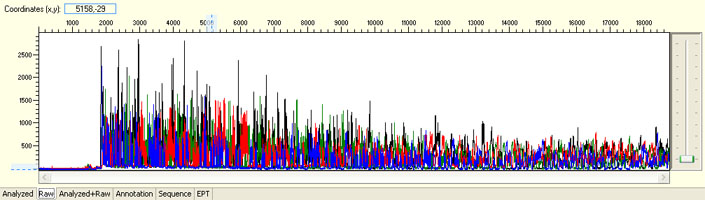
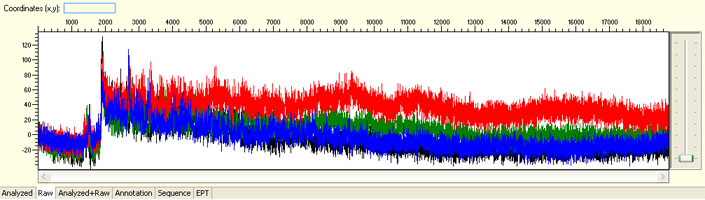
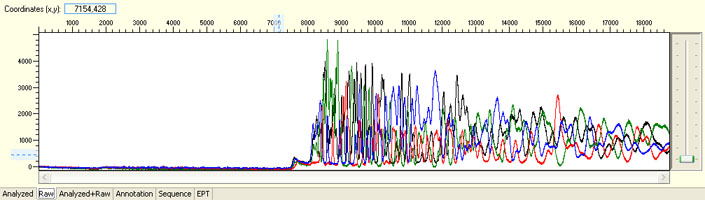
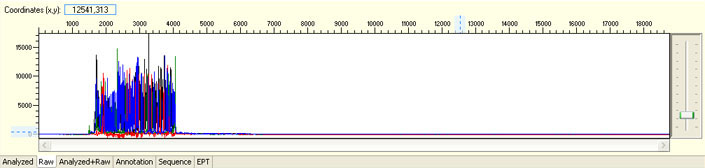
Overall noisy sequence with weak raw signals
Possible Causes
- Not enough DNA template
- Presence of inhibitors
- Low priming efficiency
- Sub-optimal cycle sequencing annealing temperature
Possible Solutions
- Quantify DNA and follow our sample submission guidelines to prepare premixed samples
- Purify DNA before adding into premixed sample
- Use new aliquot of primer or re-design sequencing primer
- Optimize cycle sequencing conditions and submit purification & run samples
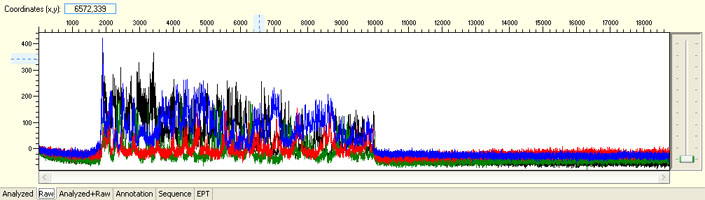
Overall noisy sequence with strong signal
Possible Causes
- Multiple templates
- Non-specific priming sites
- Contaminated template/primer
- Multiple primers
- Primer with N-1 contamination
Possible Solutions
- Resubmit pure sample
- Re-design sequencing primer
- Use new aliquot of template/primer
- Ensure only one primer is used at a time, either forward or reverse, NOT both
- Order quality guaranteed primers from CPOS Oligo Ordering Services
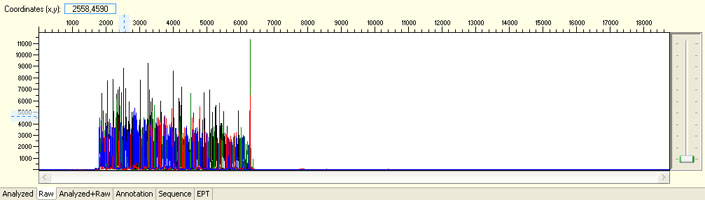
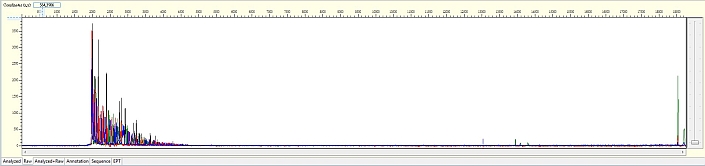
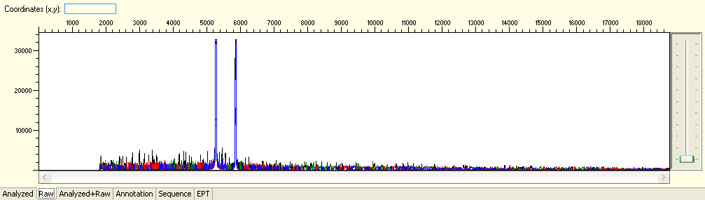
No sequence read with raw signal below 100
Possible Causes
- Insufficient DNA template
- Insufficient Primer
- Poor/No primer annealing
- Inhibition by contaminants
Possible Solutions
- Quantify DNA and follow our sample submission guidelines to prepare premixed samples
- QC DNA on an agarose gel
- Re-design sequencing primer
- Clean the sample before submission
Delayed read start with initial irregular spacing and/or presence of large peaks before sequence read
Possible Causes
- Capillary blockage
- Capillary overloaded with DNA/protein/salt or other contaminants
Possible Solutions
- Contact platform specialist to check capillary performance
- Quantify DNA and follow our sample submission guidelines to prepare premixed samples
- Purify DNA before adding into premixed sample
- QC DNA with a Nano-Drop Spectrophotometer
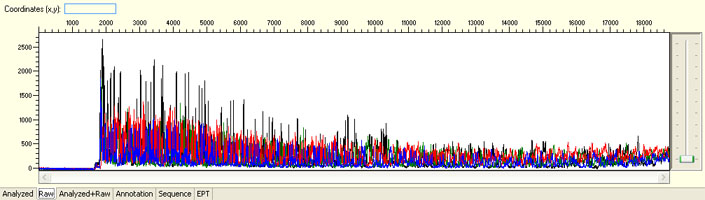
Large raw signal spike
Possible Causes
- Bubbles forming in the capillaries during electrophoresis
Possible Solutions
- Request sample rerun
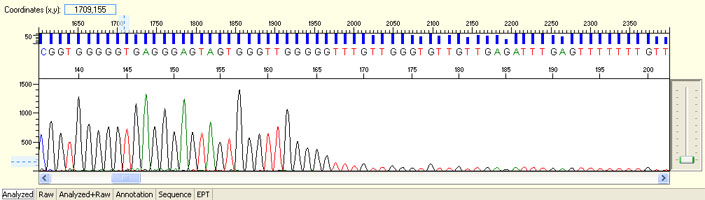
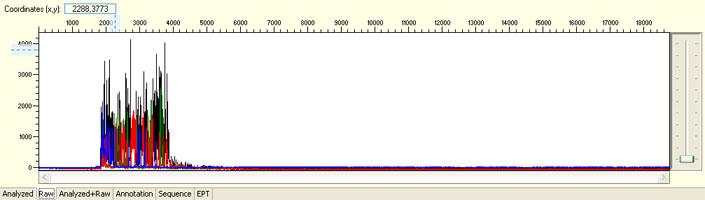
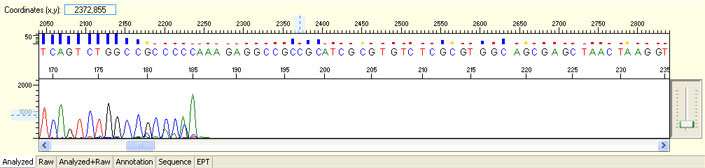
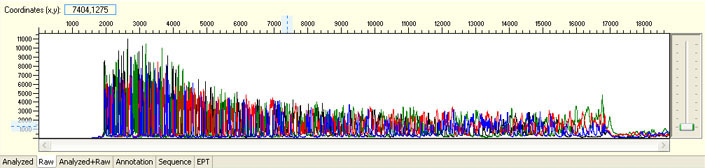
Unexpected read beyond expected length or noisy baseline
Possible Causes
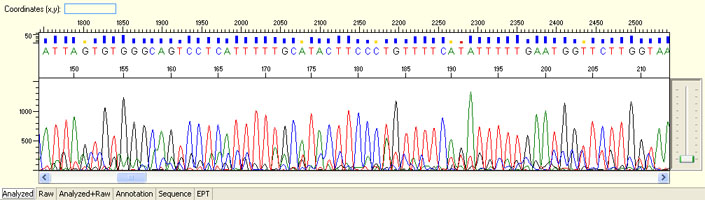
- Cross-talk from neighbouring capillary fluorescense
Illustrated is the effect of cross-talk for a template of 180bp PCR product. Sequence reads beyond 180bp are signals emitted from the neighboring capillary.
Possible Solutions
- Request sample rerun
Cross talk will not affect samples with strong signal, but may affect those with weak or no signal.
Since cross talk is hard to determine without knowing the neighbouring sample intensity, please feel free to consult platform staff for inspection if necessary.
Unexpected broad peak starting early in the sequence
Possible Causes
- Capillary deterioration
Possible Solutions
- Request sample rerun
Capillary deterioration is hard to detect without comparing different runs. Please be assured that CPOS staffs are constantly monitoring every run to detect possible capillary deterioration as early as possible. Affected clients will be contacted and samples will be rerun at no cost as soon as possible.
Contact
Ms CHAN, Joyce
Ms TSE, Christine